
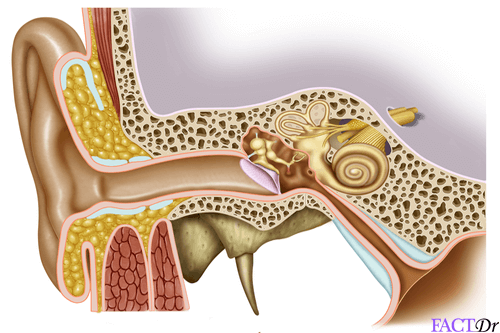
Most children older than 6 years have outgrown this problem and their frequency of ear infections should drop substantially. This is another reason that children are so prone to middle ear infections. The horizontal course of the Eustachian tube also permits easy transfer of bacteria from the nose to the middle ear space. Thus, bottle-feeding should be performed with the infants head elevated, in order to reduce the risk of milk entering the middle ear space. It runs horizontally, rather than sloping downward from the middle ear. Interestingly, the anatomy of the Eustachian tube in infants and young children is different than in adults. Since children in daycare are highly prone to getting upper respiratory tract infections, they tend to get more ear infections compared to children that are cared for at home. Also, they may have adenoid enlargement that can block the opening of the Eustachian tube. Young children (especially ages 1 to 6 years) are at particular risk for Eustachian tube dysfunction, serous otitis media, and acute otitis media because they have very narrow Eustachian tubes.

Rarely, Eustachian tube blockage may be the sign of a more serious problem such as nasal polyps, a cleft palate, or a skull base tumor. Obesity can also predispose a patient to Eustachian tube dysfunction because of excess fatty deposits around the passageway of the Eustachian tube. For reasons which are unclear, the incidence of allergies is increasing in the United States. In many areas of the country, nasal allergy (allergic rhinitis) is the major cause of Eustachian tube dysfunction. Pollution and cigarette smoke can also cause Eustachian tube dysfunction. Illnesses like the common cold or influenza are often to blame. This can occur when the lining of the nose becomes irritated and inflamed, narrowing the Eustachian tube opening or its passageway. Should bacteria contaminate this fluid, a middle ear infection may result, called acute otitis media.Ĭhronic blockage of the Eustachian tube is called Eustachian tube dysfunction. Long-term blockage of the Eustachian tube leads to the accumulation of fluid in the middle ear space that further increases the pressure and hearing loss. When it becomes stretched inward, patients often experience pain, pressure, and hearing loss. The eardrum is thin and pliable, like plastic wrap, and is densely innervated. The lining of the middle ear absorbs the trapped air and creates a negative pressure that pulls the eardrum inward. Blockage of the Eustachian tube isolates the middle ear space from the outside environment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
